There is no doubt that free Wi-Fi is great. But the public network hides many harms, even the risk of losing all the funds in the bank account.
We have collected the most critical tips to ensure that you will not become a victim of online fraud when using public Wi-Fi access.


The only foolproof way to protect yourself from data theft is to use mobile data for online purchases or online banking. For the security of your account, a few megabytes is a reasonable price.

By turning off Wi-Fi, you can solve three problems immediately: rapid battery discharge, automatic connection to fraudulent networks, and annoying advertising emails. To further protect the latter, please add an extension called DoNotTrackMe to your browser-it will not let the device track your movement.

A VPN or virtual private network allows you to remain anonymous while surfing the Internet: the website you enter will see the virtual network IP instead of your virtual IP.
However, most of these networks are paid and will slow down your connection. However, the price is usually not high, and most VPN providers still provide free services.

Most devices will automatically remember and connect to hotspots they have used at least. Frauds can use the same name to create their own access points, which can access your profile data and even access your financial status through certain tricks.


Hackers often use networks with names similar to existing networks nearby. The only difference is that a real hotspot requires payment or authorization/password, while a fake hotspot can be used for free. Therefore, before connecting to a free network, ask for the owner’s name.

Always use the latest antivirus version. There are new ways of hacking almost every day, and your antivirus software should be kept up to date. In addition, the antivirus software will warn you that there may be false hotspot connections.

A network that can be connected without any other actions may be a fraudulent network. For security, please select a hotspot that requires you to enter the password sent to your phone as a text message. This will protect you from criminals copying free internet names.

Although it seems that you shouldn’t write the password in the device, many people still do. This carelessness makes it easier for criminals to access your data. If you still want to store passwords on your media device, please at least use a password manager that encrypts the information in it.

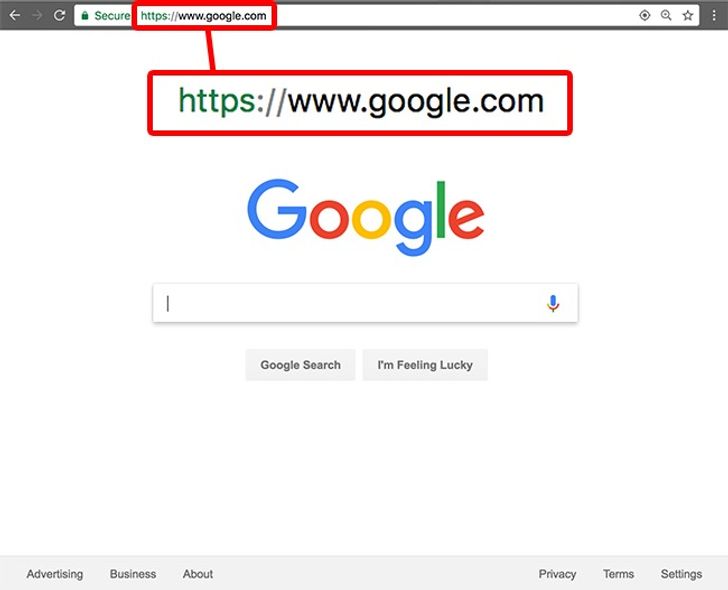
Fake networks may also redirect you to well-known websites, but those websites are actually only collecting your personal data. If you see any strange characters in the URL of a familiar website, it most likely means that the website is not authentic. Google.com and ɢoogle.com are not the same. Make sure to use a reliable and safe browser, because a good browser will detect such discrepancies and issue warnings.


A secure connection is easy to identify: the URL starts with https:// instead of the usual http://. Some websites (such as Google) always use a secure connection to transfer data.
If you want all websites to be safe, consider installing the HTTPS Everywhere extension that is compatible with all popular browsers.
