At present, the most widely used Intel CPU is marked with a very recognizable model. So what are the differences between i3, i5, and i7 processors? How should consumers choose when buying?

Purely speaking, you can simply think that Intel Core i7 is better than Core i5 than Core i3. First of all, i7 does not mean that it is a 7-core processor, the name just means its relative performance. Normally, Core i3 has only dual-core models, while Core i5 and Core i7 series have both dual-core and quad-core models, and quad-core performance is usually better than dual-core.
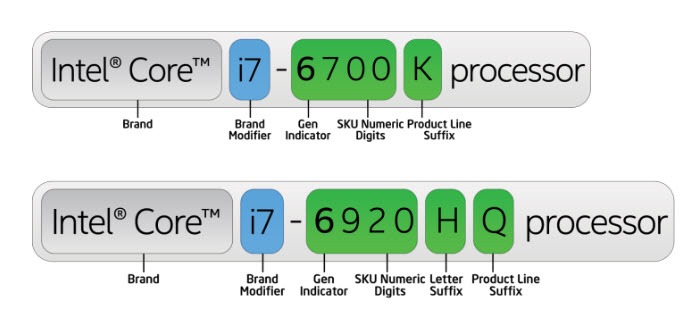
The “family” of chipsets released by Intel, such as the sixth-generation Skylake family or the older fifth-generation Haswell family, each of which has corresponding Core i3, Core i5 and Core i7 series CPU products. You can judge which generation of products it belongs to by the first position of the specific model name of the CPU. For example, Core i3-5200 belongs to the fifth generation of products.
The last three digits of the CPU model can be used for simple CPU performance and functional feature comparison, for example, Intel Core i3-5350 is better than Core i3-5200.
You may have noticed that there are many suffixes for Intel CPU models. The common ones include U, Y, T, Q, H, and K, etc. We will explain the meanings below:
U: Represents low voltage, 15W heat dissipation, mainly used for ultrabooks and thin and light notebooks.
Y: stands for ultra-low voltage, heat dissipation power consumption is 10W, this kind of processor is mainly used for two-in-one products.
T: Represents a desktop processor that has been optimized for power.
Q: It represents a quad-core physical core, but the i7 series of notebooks are not necessarily quad-core. There are also low-voltage or ultra-low-voltage dual-core four-thread products.
H: It means using Intel’s better high-performance graphics display unit.
K: Unlockable overclockable version of the CPU.
The understanding of the letter suffix in the CPU model can help you quickly understand the CPU characteristics, without the need to read the actual specifications in detail. Of course, it is recommended to check the product details of the specific model at ark.intel.com before making the final purchase decision.
【Hyperthreading: i7> i5> i3】
As mentioned above, the CPUs belonging to U and Q models use physical cores, while other models/types use virtual core technology, which is officially called hyper-threading technology. In layman’s terms, hyper-threading allows a single physical core to be used as two virtual cores, so that it is not necessary to activate the second physical core (which may require more system power) to participate in computing when performing multitasking.
A dual-core processor with hyper-threading technology will have 4 virtual cores at the same time, making the calculation faster. But please note that the physical core is faster than the virtual core, so in general, a quad-core CPU will be more efficient than a hyper-threaded dual-core CPU.
Both the Intel Core i3 series and the Intel Core i7 series support hyper-threading technology, while the Intel Core i5 series does not support hyper-threading.

【Turbo Boost: i7> i5> i3】
On the other hand, Intel Core i7 and Intel Core i5 series both support Turbo Boost, while Intel Core i3 does not support Turbo Boost.
Turbo Boost is Intel’s proprietary technology, which can intelligently adjust the clock frequency of the processor. This technology can be understood as automatic overclocking. When Turbo Boost is turned on, the CPU will automatically adjust the main frequency of the CPU according to the current amount of tasks, giving full play to the strongest performance of the CPU during multitasking, and the greatest energy-saving advantage during light tasks.
Turbo Boost improves the efficiency of resource-intensive software such as video editing and video games, but has no obvious effect on daily web page visits and light applications such as Microsoft Office.
[Cache size: i7> i5> i3]
Except for Hyper-Threading and Turbo Boost, the main difference between the above three series of CPUs is the difference in cache size. We can understand the CPU cache as the processor’s private memory. The larger the cache, the higher the efficiency.
The Core i3 cache limit is 3MB, the Core i5 series cache is between 3MB and 6MB, and the different models of the Core i7 series cache is between 4MB and 8MB.
[Display chip: HD, Iris and Iris Pro]
Since CUP began to integrate graphics chips, this has become an important decision point for users when purchasing CPUs. Intel has 3 levels of display processing units, namely: Intel HD, Intel Iris and Intel Iris Pro.
You can usually see expressions like Intel HD 520 or Intel Iris Pro 580, for example: Intel Iris 550 is better than Intel HD 520, but Intel HD 530 is better than Intel Iris 550, and Intel Iris Pro 580 is better than Intel HD530. , It seems to make people more trapped.
How do ordinary users choose? In fact, everyone only needs to pay attention to the fact that the processor model with H at the end ,which uses a high-performance display processing unit.
Core i3: An economical choice for basic users, suitable for ordinary web browsing, Office, video phone and social applications, not for gamers and professionals.
Core i5: The first choice for intermediate users. It can balance performance and price. If you use HQ or Q series models with professional graphics processors, it is also very suitable for games.
Core i7: Professionals.





