Wireless charging is “OUT”?
60W, 80W, 120W, 200W… In the field of mobile phone charging, speed has always been the common pursuit of all manufacturers!
However, speed alone cannot satisfy the “spiritual needs” of the masses. For example, what about playing mobile phones while lying down or squatting? In addition to speed, convenience is also very important!

Here comes the real convenience! Earlier this morning, Xiaomi officially announced the “Space Charging” technology. You don’t need to put it on the charging stand, you can charge your phone “automatically” and “wirelessly” as soon as you enter the house.
👇👇👇True wireless charging is here👇👇👇
Today tom will take you to see what is going on with this latest “black technology”, and, is it safe…?
Put one in the house, the whole house can be charged
The core of Xiaomi’s air charging technology lies in spatial positioning and air energy transmission.

The air charging pile has 5 phase interference antennas, which can locate the mobile phone in millisecond space, accurately detect the position of the mobile phone, and there is no fear of disconnection when walking!

The positioning is successful, how to transmit it?
The air charging pile also has a built-in phase control array composed of 144 antennas, which transmits millimeter waves to the target mobile phone through beamforming.

This technology is bigger, you can even refer to the four-sided phased array radar of the 055 destroyer-except for the receiving end, the receiving end of the air charging is not in its (transmitting end) itself, but on the mobile phone end.
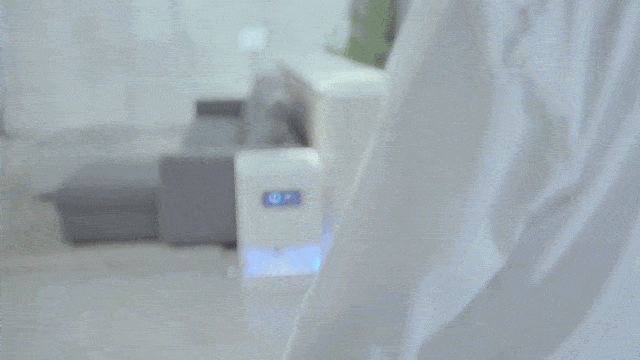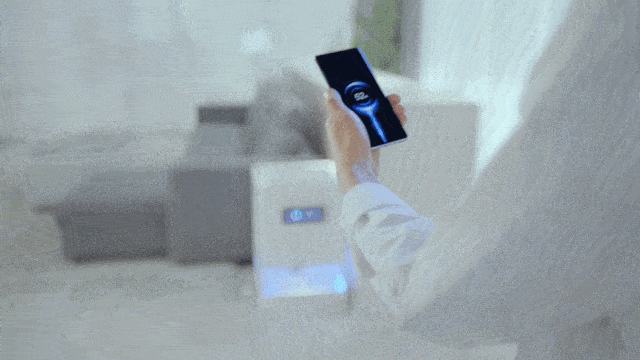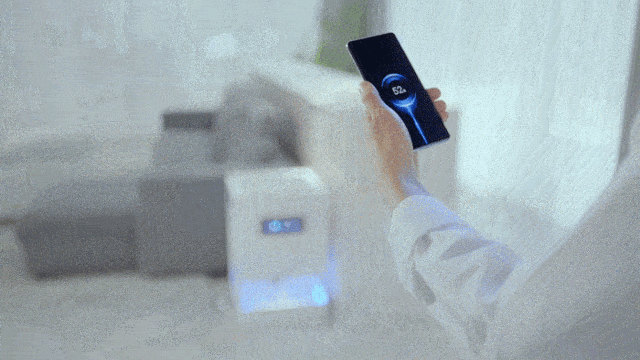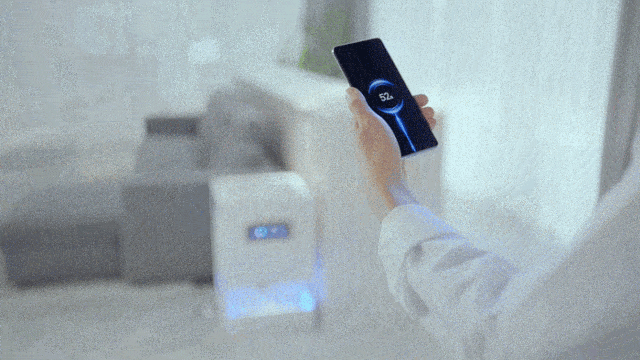
For this reason, Xiaomi has self-developed a miniaturized antenna array, and stuffed the beacon antenna and receiving antenna array into the Xiaomi mobile phone with an inch of gold.
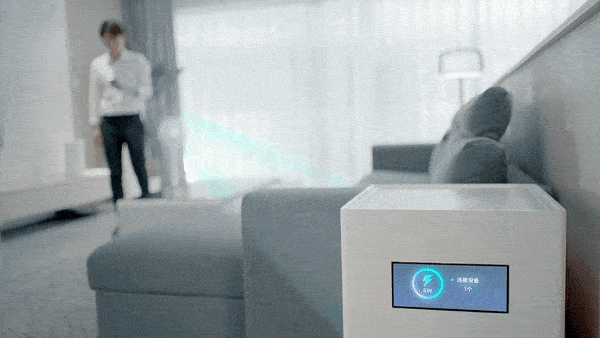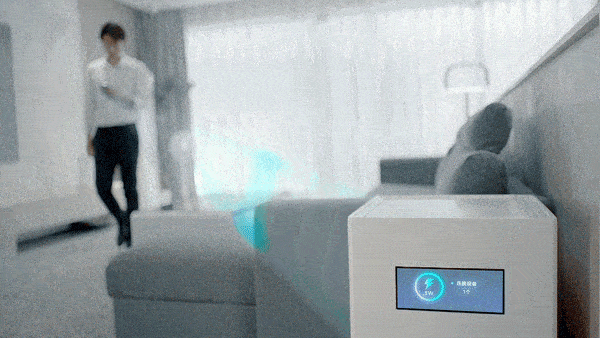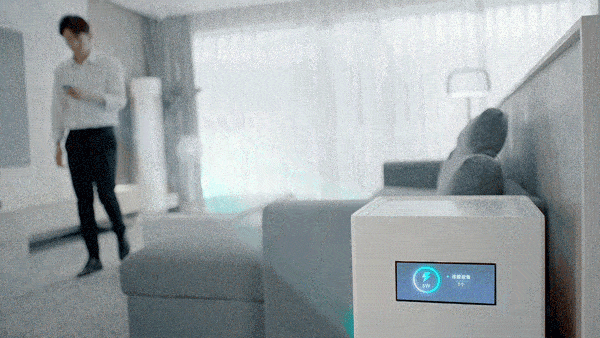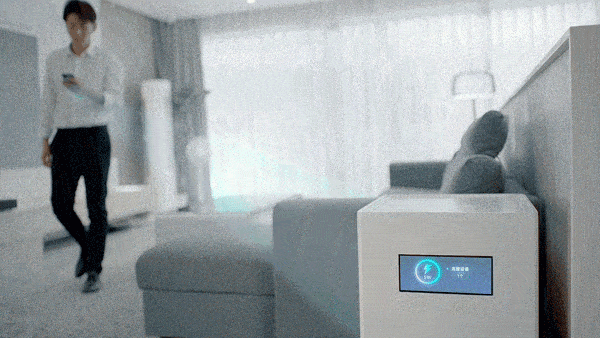
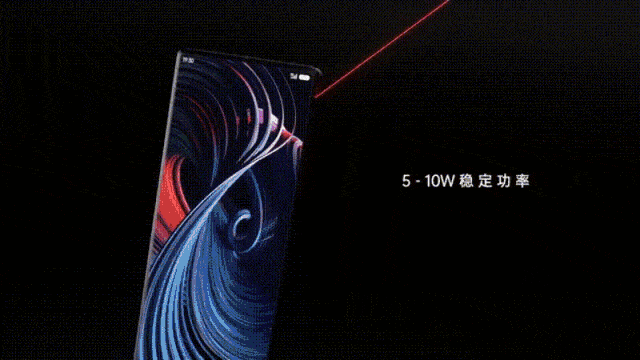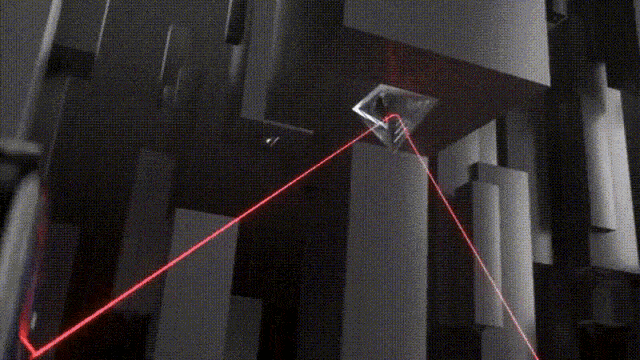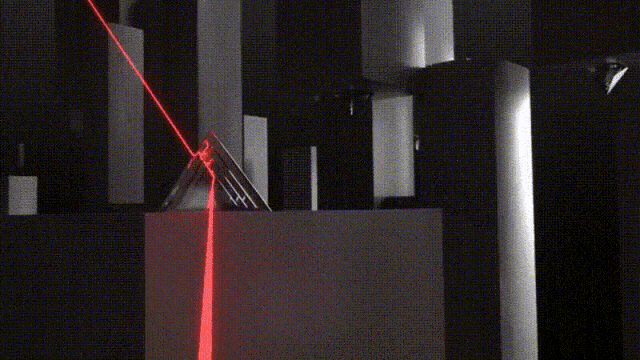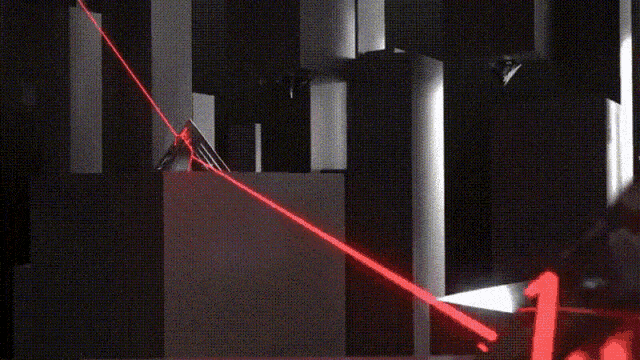
The beacon antenna is responsible for broadcasting location information. The 14 antennas form a receiving antenna array, which converts the millimeter-wave signal emitted by the charging pile into electric energy, thereby realizing 5 watts of long-distance (within a few meters) charging in the air, full of technology.

Also, Xiaomi has managed to charge multiple devices at the same time (each device has 5 watts), even if there are foreign objects, it will not reduce the charging efficiency, and the environment is extremely adaptable.

On the same day that Xiaomi announced the space charging technology, Lenovo’s Motorola also released a space charging solution.
Moto’s solution also supports long-distance wireless charging, and also supports simultaneous charging of multiple devices. However, the Moto solution currently only shows a transmission range of 1m, and the charging will be disconnected when there are obstacles such as the palm. Obviously, there is still a certain distance from Xiaomi’s “air charging”.
In addition to the specific plans of the previous two, tom also turned to the patent office’s official website for an air-to-air charging patent published by Huawei: “A long-distance laser automatic charging system with protection function”.
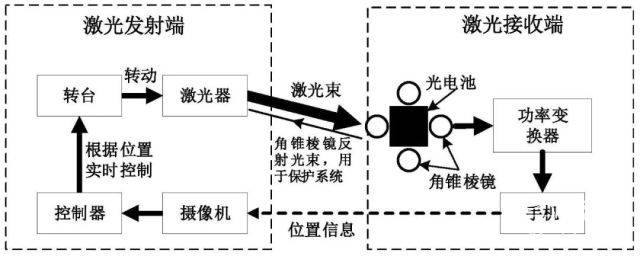
Although the patent description is extremely perfunctory, it can be seen that the principle of the solution is quite different from that of Xiaomi and Moto. Unfortunately, no finished product has appeared in front of the public so far.
Three technologies to achieve “air charging”
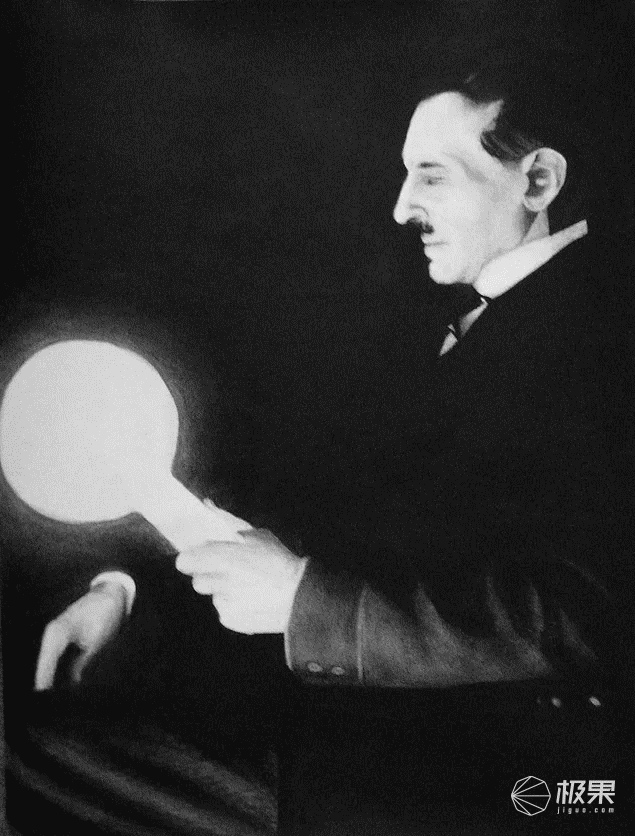
Although wireless power supply has only been widely used in recent years, in fact, as early as the Chicago World Expo in 1893, Nikola Tesla was able to light up a light bulb without wires.

More than 100 years have passed, and there are now more wireless transmission methods. From the mainstream point of view, there are roughly three. The first is the magnetic induction type, which is widely used in various wireless charging devices (such as mobile phones, electric toothbrushes, etc.).

Its principle is similar to that of a separate transformer, which first converts electrical energy into magnetic energy and then back to electrical energy to complete power transmission. When applied to low-power devices, it has high safety and high charging efficiency.

The second is the microwave radiation type. The principle of this method is to convert electrical energy into electromagnetic waves through an antenna and then conduct long-distance transmission. This method has the characteristics of long transmission distance and high power. In an experiment in 2008, a 2.4 GHz microwave was used to complete a high-power power supply for receiving equipment far away 148 kilometers away. But the problem with this technology is that the transmission efficiency is very low, the radiation is large, and the impact on the human body is large.
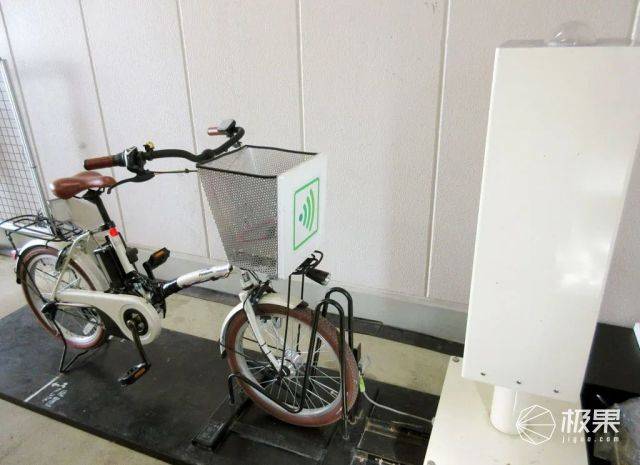

In Japan, “microwave charging stations” are charging electric bicycles (experimental stage)
However, Ossia’s Cota technology is a bit more advanced. Although they use this technology, they can determine the location of electronic devices in the house through Wi-Fi, and use radio frequency antennas to accurately charge electronic devices, which also meets safety standards. The transmit power is only 1W.
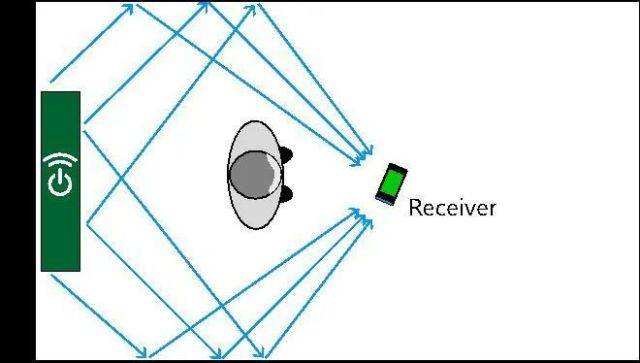

The third method is non-radiative resonance magnetic coupling. This is the latest of these three technologies. It is a new method invented by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 2007. The principle is to use two or more vibration systems. When they have the same frequency and the coupling degree reaches the strongest, wireless power transmission can be realized.

Scientists at MIT lit a 60W bulb two meters away
And, through research, it is found that the propagation distance of this method can reach several meters, and the transmission efficiency is high, and the directivity is not strict. The most important thing is high safety, and the amount of radiation is within a safe range.
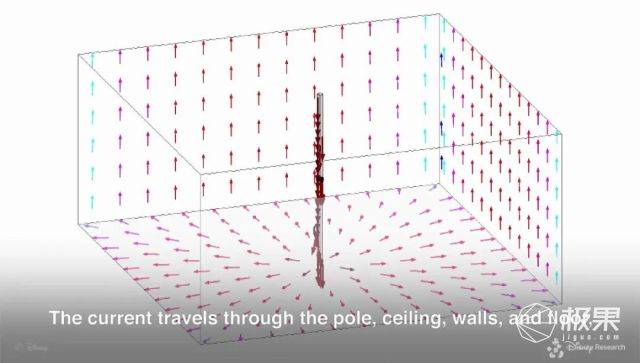
But in the beginning, this technology is difficult to safely and efficiently charge the various small devices in the house. But after two improvements, great progress has been made. The first time it was improved by the Disney Research Institute (yes, that is the Disney in the wonderful house), they used “quasi-static cavity resonance” (QSCR) technology to power various small electronic devices in the house.
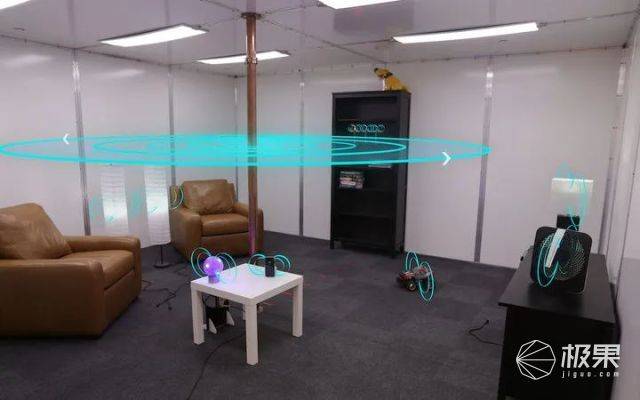

But this technology is actually very troublesome. It needs to place a huge “conductor rod” in the house and also has requirements for the wall. In short, a magnetic field must be formed inside the house.
The second time it was improved by the University of Tokyo and invented the “Multimode QSCR” (Multimode QSCR) technology based on the Disney Research Institute. This set of equipment can provide tens of watts of power, enough for some small equipment, and there are almost no dead ends in the house.
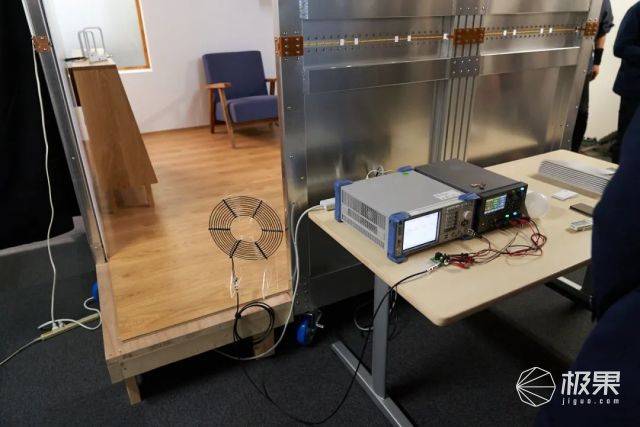

Although this technology eliminates the need to set up huge metal rods in the house, it still requires metal walls and capacitors placed in the walls to allow the resonance power transmission equipment to complete the work with low loss.
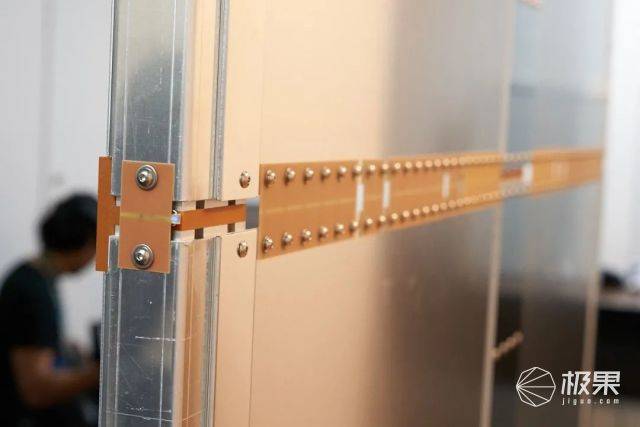

However, there are still many problems. For example, the power receiving device needs a large coil… Therefore, this technology still has many difficulties waiting to be overcome.
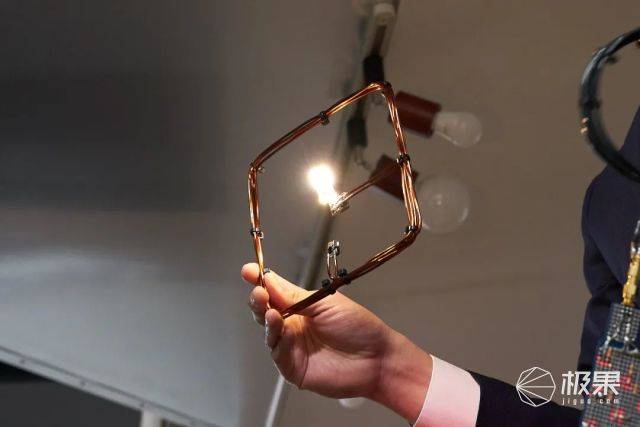

Judging from the video released by Xiaomi, the technology it uses is similar to the second-microwave radiation type, but the difference is that it emits millimeter waves. Therefore, it may also use more advanced new technologies. But no matter what it is, if it can operate like the video, it is a breakthrough. But how about security?
Is “air charging” harmful?
Although “air charging” is convenient, more people worry about the safety of use-is it harmful to the human body?
After all, “Can the mobile phone be charged by the bedside?” This matter is still being debated…

And “charging in the air” means that the whole house is full of “radiation”? Especially when there is static electricity on your body in winter, is it still “electrocuted”?

However, Zhang Jialiang, chief scientist of OPPO VOOC flash charging, said before, “There are no technical obstacles to air charging or even long-distance wireless charging. When it is commercialized, it has legal and regulatory requirements, as well as equipment safety and personal safety requirements.”.

(Zhang Jialiang) However, since this is still a new technology, there are currently no corresponding regulations and standards. tom carefully looked at Xiaomi’s “air charging” technology. It did not announce the transmission power and frequency of the air charging pile, so it can’t directly judge whether it’s harmful. It is worth mentioning that the China Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued the “Announcement on Micropower Short-Range Radio Transmission Equipment” in November 2019, which put forward all micro-power radio equipment transmission requirements, including the application scenarios of the equipment, and the transmission frequency, distance, power, etc. Wait.

Among them, the equipment with the highest frequency reaches 702.0-798.0MHz, and the corresponding transmission power is ≤50mW. And Xiaomi’s “air charging” uses millimeter-wave signal transmission (the millimeter-wave frequency range is generally considered to be 26.5 ~ 300GHz). By comparison, it seems that the transmission power of the Xiaomi air charging pile will not below.
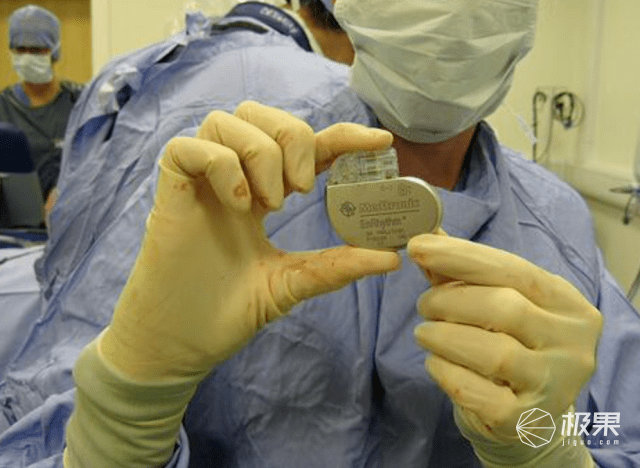
Of course, if the Xiaomi air charger is to be listed, it must meet the corresponding international standards! It must be mentioned that users of medical equipment such as pacemakers still need to pay extra attention.
Charging is not only convenient
tom remembers that OPPO released the same “space charging” technology on April 1st last year, but it was just an April Fools’ Day joke.
But this time Xiaomi is really moving. According to the official, its “air charging” technology can also charge smartwatches, bracelets, and other wearable devices in the air; even small smart home products such as speakers and desk lamps can achieve wireless power supply, completely free from the shackles of wires, and truly realize wireless in the living room. At present, it is only at the “conceptual stage”. It is estimated that it will take several years to get the actual product… But tom is already looking forward to it!

What else can be done with this high-tech “charging in space”? Some people need to replace the battery of the medical equipment implanted in the body. With air charging, they can charge without taking out the equipment. Research on laying charging equipment under the road so that electric vehicles “always have electricity” is continuing in various countries. This new technology can bring us more than just “convenience”.




